The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in 2025: The increase in digital transformation across industries has led to a rise in cyber threats. As businesses embrace cloud computing, AI, and IoT, the attack surface has expanded, making cybersecurity more critical than ever.
The Impact of Cyberattacks: Discuss how high-profile data breaches, ransomware attacks, and cyber espionage are disrupting industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. The financial and reputational damage of these attacks is growing, highlighting the need for stronger defenses.
1. The Evolution of Cybersecurity
- Past Challenges: In the early days, cybersecurity mainly focused on securing networks and protecting against viruses. Traditional firewalls and anti-virus software were the primary tools.
- Current Threat Landscape: Today’s cybersecurity involves a multi-layered approach with endpoint protection, threat intelligence, data encryption, and more. The introduction of AI and machine learning into threat detection systems has made these solutions more proactive.
- Technological Advances: Technologies like biometric authentication, encryption algorithms, and advanced security operations centers (SOCs) have revolutionized cybersecurity practices.


2. Emerging Cyber Threats in 2025
- AI-Powered Attacks: Hackers are now using AI to create smarter malware that can learn from its environment, making it harder to detect. AI can automate attacks, making them more rapid and widespread.
- Deepfakes: As deepfake technology improves, attackers can create realistic fake videos or audio recordings to impersonate people in positions of authority, leading to phishing attacks, fraud, and identity theft.
- Ransomware: Ransomware attacks are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure such as healthcare systems and energy grids. These attacks often come with advanced encryption that locks out systems until a ransom is paid.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or unintentional actions by employees are growing threats. Insider threats can range from stealing intellectual property to accidentally compromising sensitive data.
- Social Engineering: Hackers are constantly refining techniques to manipulate individuals into giving away sensitive information. This includes phishing, spear-phishing, and vishing (voice phishing).
3. AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
- Predictive Threat Detection: AI can analyze patterns and predict potential threats before they occur. By analyzing network traffic and user behavior, AI can detect anomalies and prevent data breaches.
- AI for Automated Response: Machine learning can help automate responses to cyber threats, reducing the need for human intervention. This is particularly important in handling zero-day exploits where immediate action is crucial.
- Adaptive Security Systems: AI-based systems adapt to changing environments and evolve with emerging threats. This can help organizations stay one step ahead of hackers.
- Risk Mitigation: AI-driven solutions help companies understand their vulnerabilities by simulating attacks and testing their defenses. This proactive approach can identify weak points before they are exploited.

4. Cloud Security in 2025
- Shared Responsibility Model: When using cloud services, the security responsibility is shared between the provider and the customer. Businesses must ensure their cloud configurations are secure.
- Data Encryption: Protecting data in transit and at rest is essential. Encryption is a fundamental part of securing cloud-based assets, and encryption keys need to be managed properly to ensure their integrity.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Using IAM solutions in the cloud can prevent unauthorized access. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) are important elements of a strong IAM strategy.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Security: Many businesses are now using multiple cloud services. Managing the security of hybrid and multi-cloud environments requires integrated, scalable security solutions to ensure compliance and protect data across different platforms.

5. Cybersecurity for the Internet of Things (IoT)
- IoT Vulnerabilities: Many IoT devices lack proper security measures, such as weak default passwords or outdated software. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by hackers to gain access to networks.
- Device Management: IoT devices need to be constantly monitored and updated. Effective device management ensures that vulnerabilities are patched, and security is maintained.
- Segmentation: For greater protection, businesses should segment their IoT devices from their primary network. This way, even if a device is compromised, the damage is limited.
- IoT Security Frameworks: Emerging security frameworks, such as the IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act of 2020, aim to provide guidelines for manufacturers to enhance the security of their devices.
6. The Role of Privacy Regulations and Compliance
- GDPR and CCPA: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have set the standard for data protection. Companies must adhere to these regulations to avoid hefty fines and penalties.
- Impact of New Privacy Laws: In 2025, we expect more regions to implement stricter data privacy laws. Companies must stay compliant to maintain customer trust and protect sensitive data.
- Data Sovereignty: As businesses store more data in the cloud, the issue of data sovereignty has become more complex. Different countries have different laws about where data can be stored and who can access it.

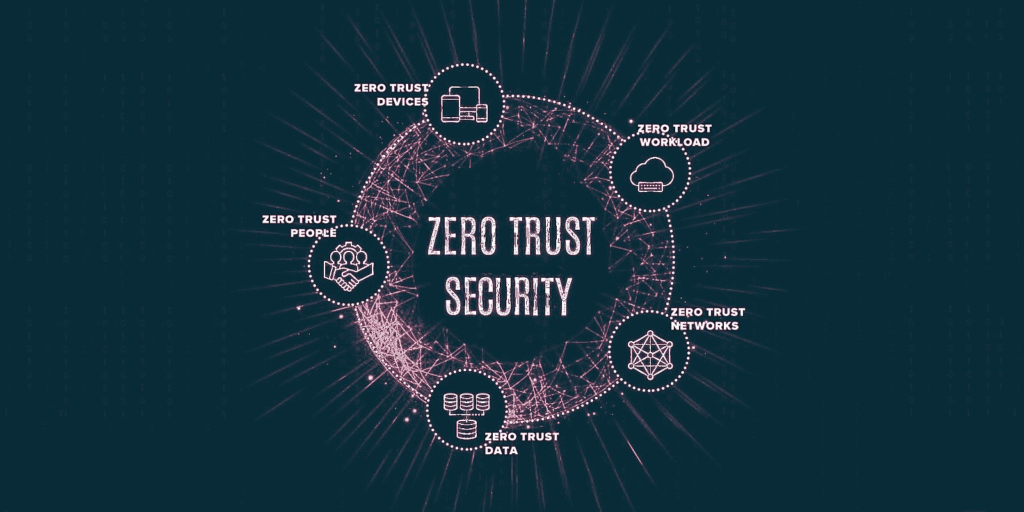
7. Zero Trust Security Model
- What is Zero Trust?: Zero Trust assumes no user or device, inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Every access request must be authenticated and authorized before access is granted.
- How It Works: Instead of relying on a perimeter-based security model (e.g., a firewall), Zero Trust focuses on continuous verification, least-privilege access, and strict identity management.
- Benefits of Zero Trust: It significantly reduces the risk of lateral movement within networks, minimizes insider threats, and makes it harder for attackers to move undetected.
- Challenges: Implementing Zero Trust can be complex, as it requires a deep understanding of network architecture and continuous monitoring. Companies need the right tools and a cultural shift towards security-first thinking.
8. Cybersecurity for Remote Work
- Securing Remote Work Environments: As more employees work remotely, businesses need to ensure secure access to corporate resources. VPNs, endpoint protection, and secure Wi-Fi are essential to protect data.
- Secure Collaboration Tools: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom are widely used for remote communication. Ensuring these platforms are secure and encrypted is a top priority.
- BYOD Policies: Many employees use personal devices for work. It’s essential for organizations to implement Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies that enforce security protocols, including anti-malware, remote wipe capabilities, and device encryption.
- Employee Awareness: Employee training on cybersecurity best practices, including recognizing phishing emails, using secure passwords, and updating software, is crucial for maintaining security in a remote workforce.

9. Blockchain and its Role in Cybersecurity
- Decentralized Trust: Blockchain offers decentralized verification, reducing the need for trusted intermediaries. This makes it harder for attackers to alter transaction records or breach systems.
- Blockchain for Secure Transactions: Blockchain is already being used in cryptocurrency transactions to ensure transparency and security. It can be extended to industries like finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain enables smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. These can automate and secure business transactions without relying on a centralized authority.

10. Future Trends in Cybersecurity
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing promises to revolutionize encryption by cracking traditional encryption algorithms. However, it also offers new methods for creating virtually unbreakable encryption.
- Cybersecurity Automation: Automation will play a critical role in reducing response times and improving threat detection. The use of Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools will become more widespread.
- AI-Driven Security Operations: Security teams will rely more on AI to monitor, detect, and respond to cyber threats in real-time. AI can filter out false alarms and prioritize the most critical issues.
- The Evolution of Ransomware: As ransomware continues to evolve, attackers are using techniques like double extortion, where they not only encrypt data but also steal it and threaten to leak it unless paid.

- Emphasize the importance of staying ahead of emerging threats by adopting a proactive cybersecurity strategy.
- Encourage businesses to implement a multi-layered security approach that incorporates AI, Zero Trust, encryption, and continuous monitoring.
- Call to action: Stay educated and prepared for the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity by continuously updating your defenses and engaging with the latest technologies.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is for general informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the content, we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of any information, nor do we endorse any specific products, services, or companies mentioned. Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, and the strategies and technologies discussed may change over time. We recommend that readers consult with a professional cybersecurity expert or conduct further research before making any decisions based on the content provided. We are not liable for any losses or damages that may result from the use of this information.
#Cybersecurity #TechTrends #CyberThreats #DataProtection #InfoSec #AIinSecurity #CloudSecurity #CyberDefense #ZeroTrust #CyberAwareness #IoTSecurity #CyberResilience #CyberSafety #DigitalSecurity #PrivacyMatters #RansomwareProtection#carrerbook#anslation
